What are hard drive partitions? Simply put they are dividers. A single physical hard drive or SSD can be divided, or partitioned, into several separate partitions. Think of a partition as a self-contained compartment within the drive that can store data.
Instead of viewing the entire drive as one massive storage space, partitioning allows an operating system (such as Windows ) to treat each partition as if it were a completely separate disk.
Hard Disk Partitions
Every hard drive (or hard disk) on your computer needs to have at least one partition. The partition defines the area of the disk that can be used for data storage. Without a partition the operating system (Windows) can’t use the drive.
The information about where each partition starts and ends is stored in the GUID Partition Table for GPT formatted disks, and in the Partition Table on MBR disks.

Disks And Drives
If you’re new to computing you may be feeling a little confused as to the difference between disks and drives. Essentially they are the same thing. The terms are generally interchangeable.
Partitioning
Partitioning means to split one physical drive into several different logical drives (sometimes called volumes). Each partition will be assigned a drive letter and appear as a separate drive (or disk) in Windows File Explorer.


Windows Disk Management
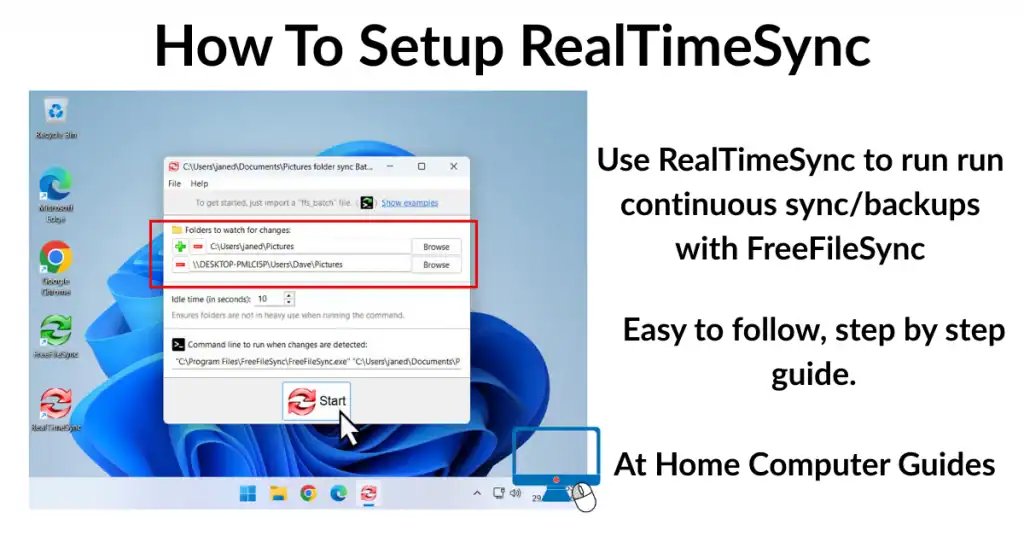
To see the partitions on your hard drives, open Windows Disk Management.
Click the Start button, type “disk management” and then click Create and Format Hard Disk Partitions.
In this example I only have a single physical disk but it’s divided into 3 partitions. This is a typical layout for most computers.
The 2 partitions at either end of the drive are used by the operating system for booting and recovery. These 2 partitions are hidden from the OS (Windows ). So they won’t appear in File Explorer, only the centre partition appears in File Explorer.
The centre partition is where Windows, all your programs and apps and all your files are stored. It’s usually referred to as the system drive, or the C: drive, since that’s where the operating system is installed and it usually has the drive letter C:.


However if you partition the drive, add anew partition, it’ll appear in File Explorer as a separate drive (or disk).
Even though they’re on the same physical drive, each partition acts independently. A new volume (partition) gets its own drive letter and can use a different file system without impacting other partitions.
It’s also possible to create hidden partitions that can’t be seen be the operating system (such as Windows), which can be used to store private and personal info on a shared PC.


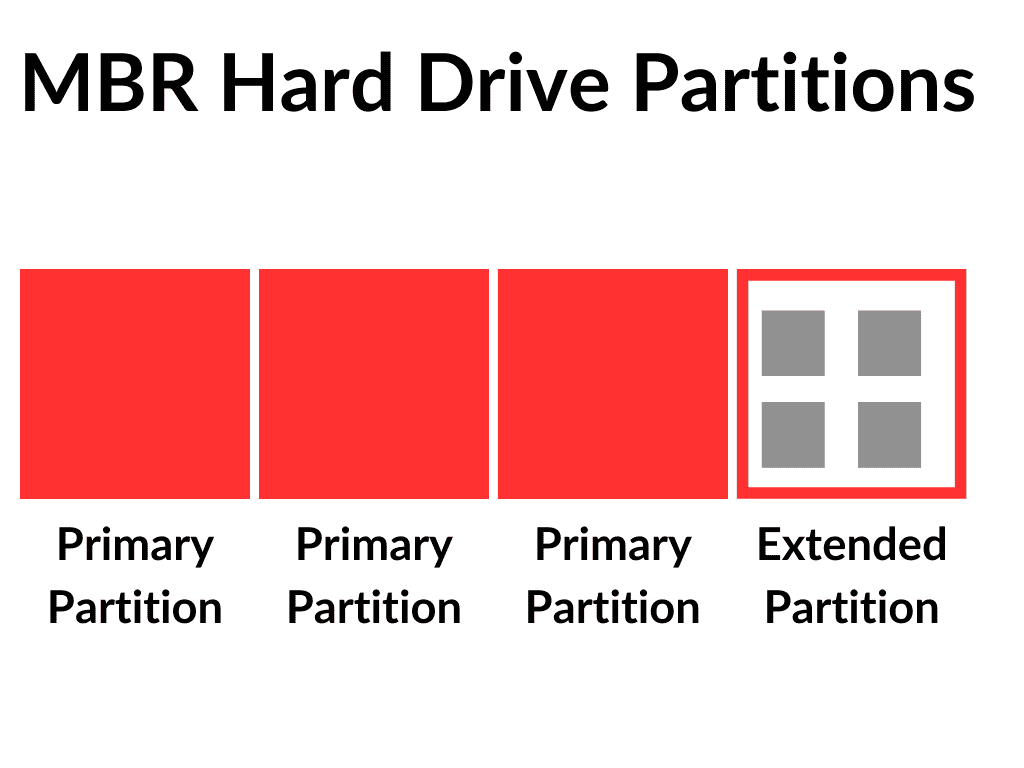
Primary, Logical And Extended Partitions.
With the older MBR (Master Boot Record) format you can only have 4 primary partitions. To get around that limitation, logical and extended partitions were created.
A logical partition resides inside what’s known as an extended partition. The extended partition acts as the container for logical partitions. Rather like a folder with subfolders inside it.
The thing to note about extended partitions is that they are actually a primary partition
So you could have 3 primary partitions and 1 extended partition. Inside the extended partition you can create several logical partitions.
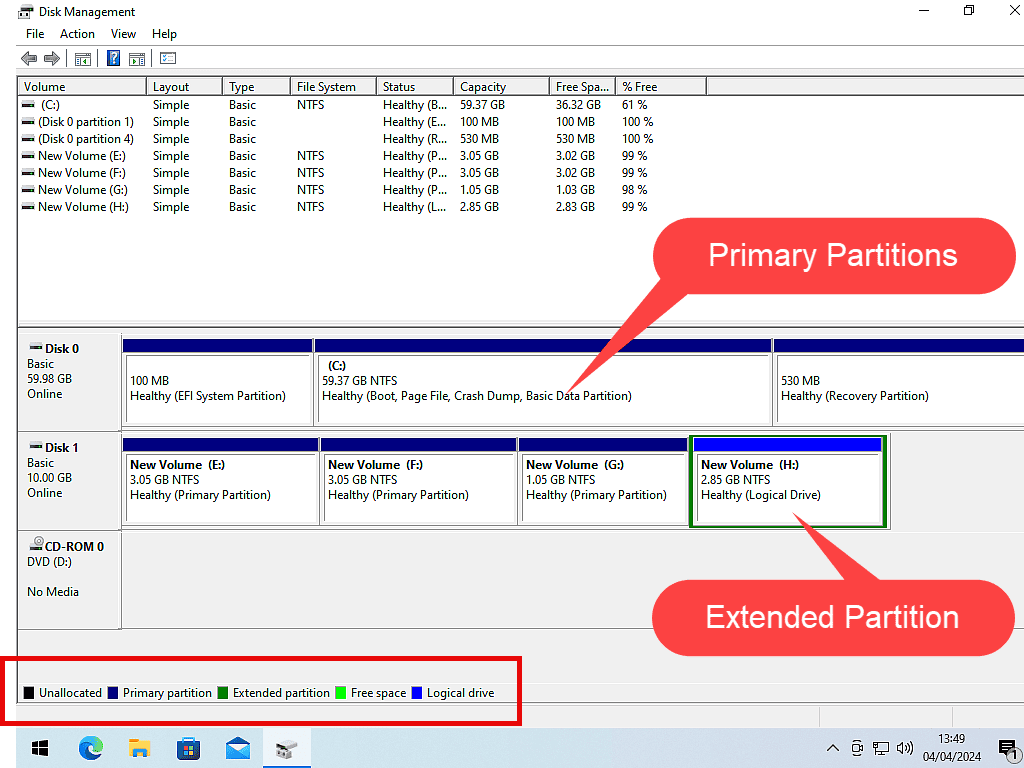
Windows Disk Management shows you size and position of each partition on your hard disks. Note the colour code key at the bottom left of the window.
Using the key code you can quickly see which partitions are primary and which are logical.
Primary partitions have a dark blue bar across the top. Logical partitions have a lighter blue bar across the top and Extended partitions have a green border
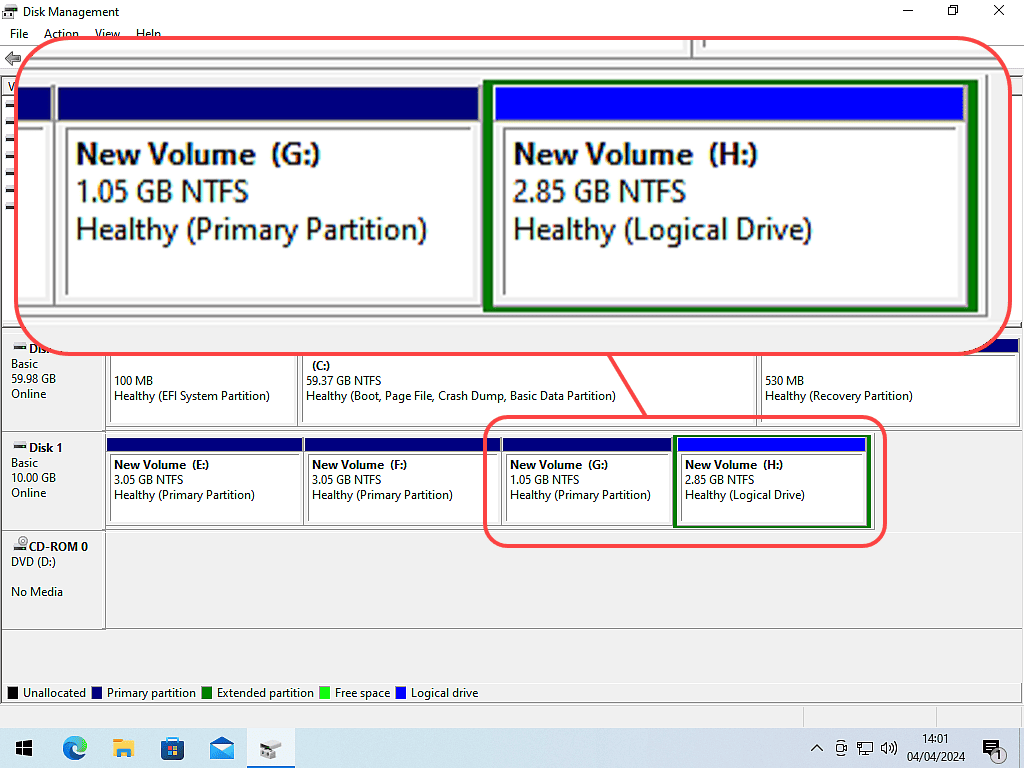
GPT Formatted Disks
GPT is the newer format style for hard disks and can support many primary partitions and so will create only primary partitions by default. Most Windows 10 and Windows 11 computers will have their disks formatted as GPT. How To Convert MBR And GPT Disks
The Difference Between Primary And Logical Partitions
The most important difference between primary and logical partitions is that operating systems have to be installed onto primary partitions.
When used for data storage you won’t really see any difference between the two types.
Why Use Drive Partitions
- Dual or Multi Booting Operating Systems. One of the most common reasons for partitioning hard drives these days to that it gives you the ability to install several different operating systems onto the same hard drive. Each OS would have it’s own dedicated partition.
- System and Data Separation. Having your data stored on a separate partition to the operating system (Windows) can help to avoid data loss when Windows inevitably goes wrong.
- Organising Your Data. You can have separate partitions for work files, games, multimedia, backups, etc., making it easier to find and manage specific types of data
Summary
Partitioning your hard drive does have certain advantages in specific use cases especially for dual booting. Generally when you want to run extra operating systems on your home PC, I’d advise you to use virtual machines since they’re easy to setup.
But booting to an OS on its own partition gives you the full power of the system, rather than sharing resources between the host and guest system in a virtual environment.
Related Posts
How To Partition A Hard Disk In Windows.
Create your own partitions. You don’t really need any special software, Windows can it all for you.
How To Move A Hard Disk Partition
Sometimes a partition will be in the wrong place on a disk. But you can move it.
Windows 11 Virtual Computer
Create a Windows virtual machine. It’s free and not that difficult to do.
Virtual machines are great for experimenting with. You can try out new operating systems, you can browse the web safely and open suspicious emails. Download new software to try it out, all without risking your host (real) computer.