Enable virtualization in your computer BIOS/UEFI in order to run virtual machines and Android emulators.
Windows 11 computers should have virtualization enabled by default, but with Windows 10 PCs it might be disabled, which leads to “Hardware virtualisation is disabled” errors when you try to setup virtual machines.
In this guide I’ll walk you through the steps to get virtualisation enabled on your PC.
Enabling Virtualization
Virtualization allows your computer’s processor (CPU) to act like several different computers at once. That lets you run a completely different operating system, like Linux or an older version of Windows, inside a window on your current PC.
The difficulty is that it has to be enabled through your motherboard BIOS/UEFI, which is outside of Windows. But we’ll get to that, the first thing to do is to check whether virtualisation is already enabled, and that’s quick and easy to do.
How To Check If Virtualization Is Already Enabled
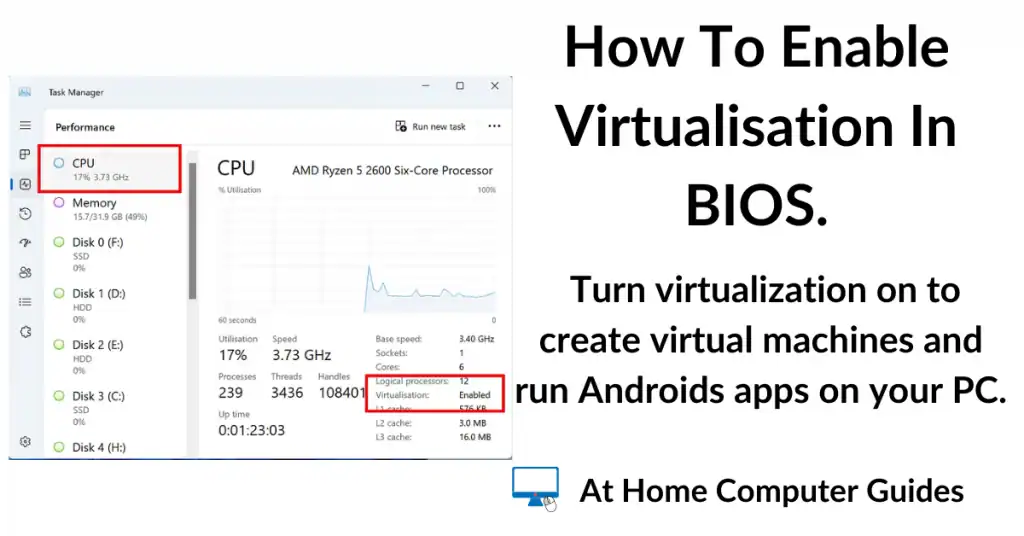
You can quickly check if virtualization is already enabled on your computer by opening Task Manager and checking on the Performance tab
- Right click on the Windows taskbar. On the menu left click Task Manager
- In Task Manager, click on the Performance tab.
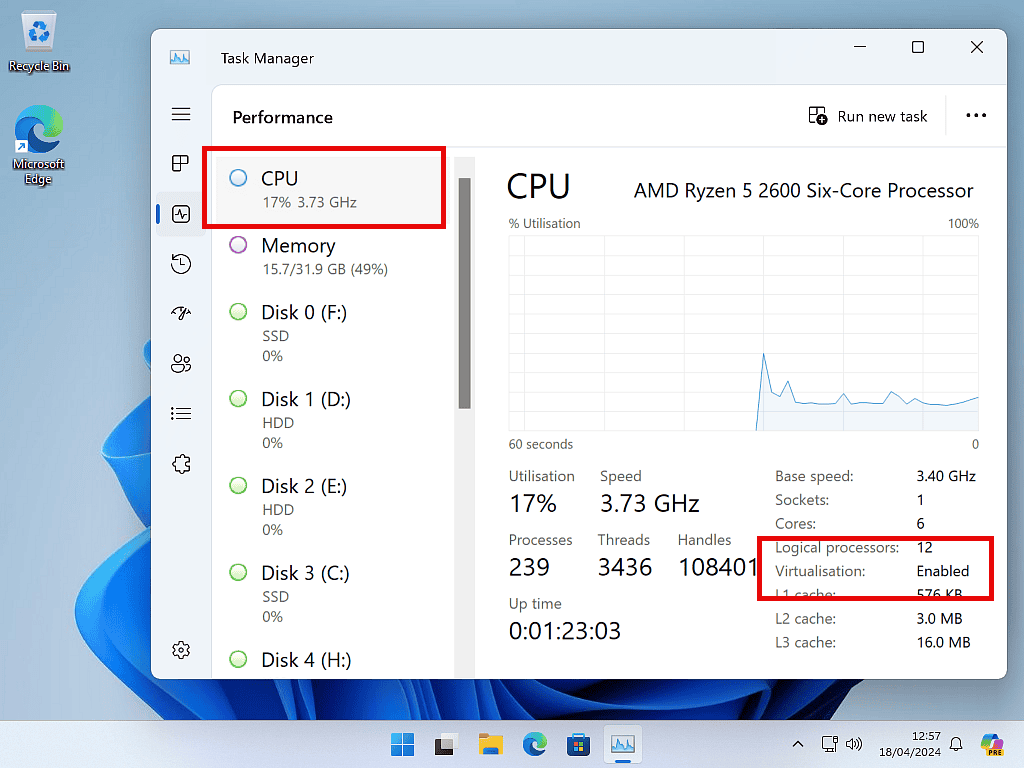
- Select the CPU (if it isn’t already) and then check to see if virtualisation is enabled or not.
- If it’s enabled then you’re good to go, but if it says disabled, or maybe not available, then you’ll need to enter the BIOS to turn on virtualization.
How To Enter The BIOS
When trying to enable virtualization the first issue you’ll encounter is getting in to your computer BIOS/UEFI. The easiest method is to to use Windows own recovery tools.
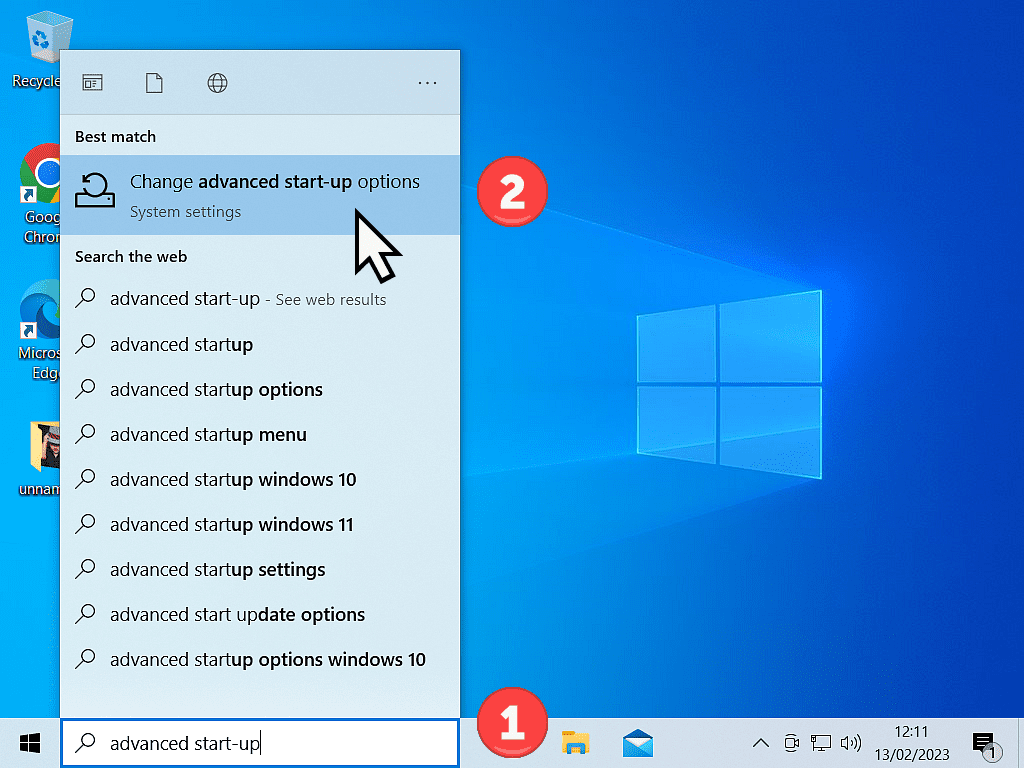
Click the Start button and type “advanced startup“ then left-click Change Advanced Start-Up Options (System Settings).
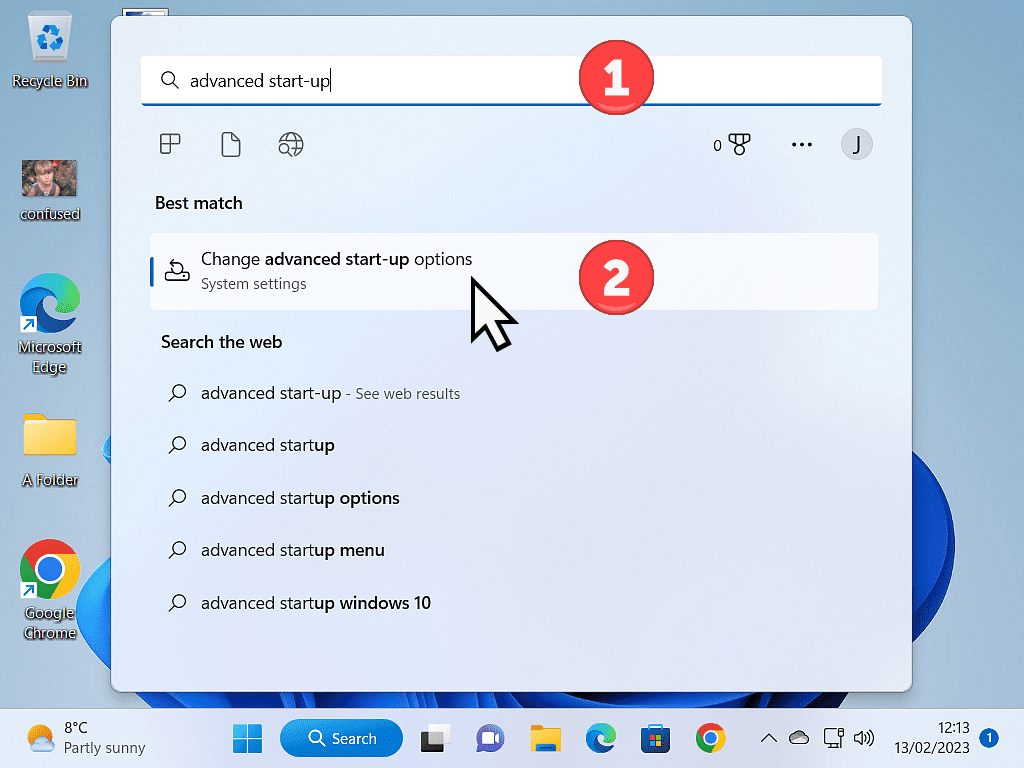
In Windows 10 – Under the Advanced Start-up section, click the Restart Now button.
And for Windows 11 – Under the Recovery Options section, click the Restart Now button.
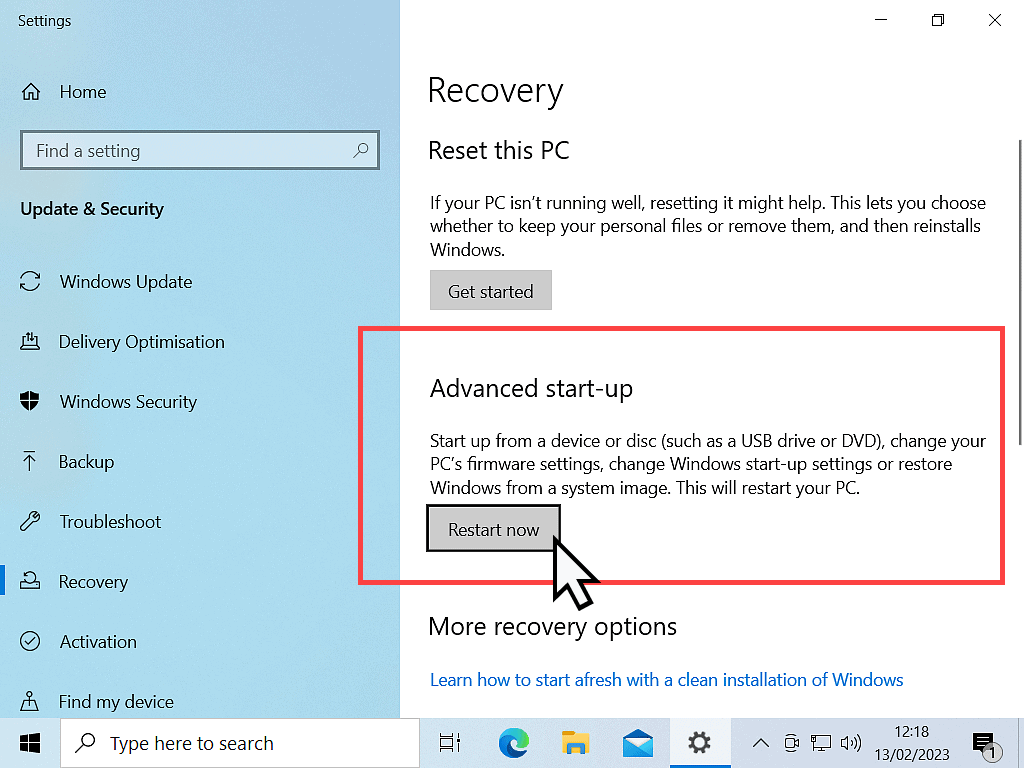
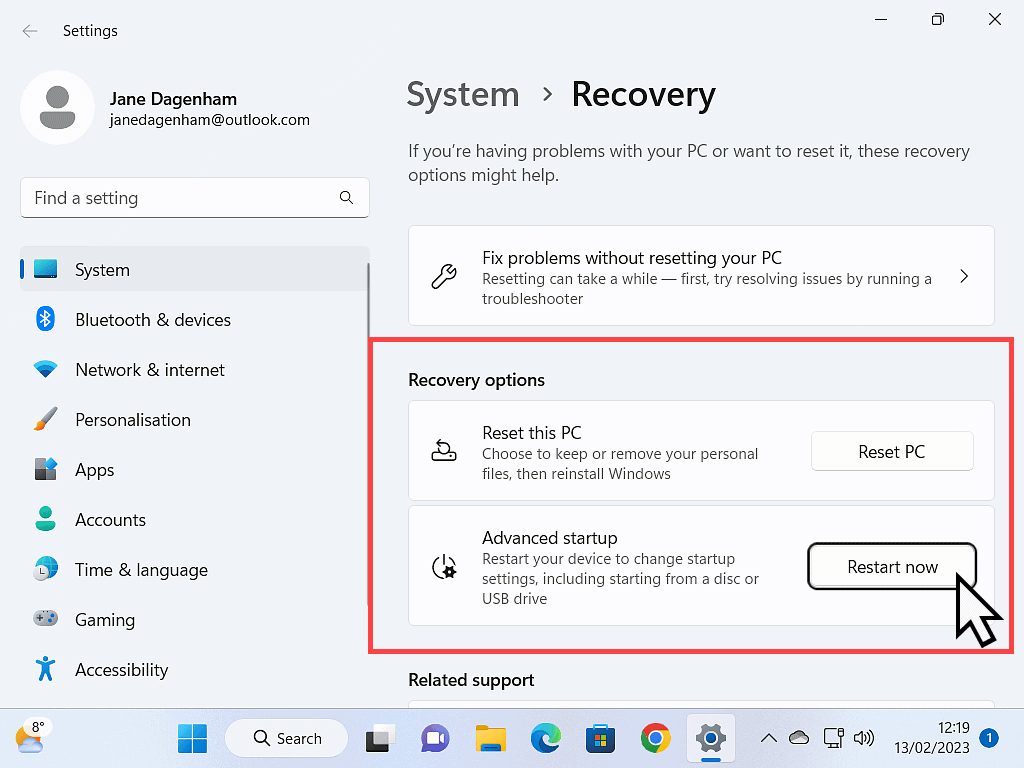
Booting Into BIOS To Enable Virtualisation
When your computer restarts you’ll be in the recovery options rather than the usual Windows environment. From here you can set the PC to open in to the BIOS, from which you’ll be able to turn on the virtualization options.
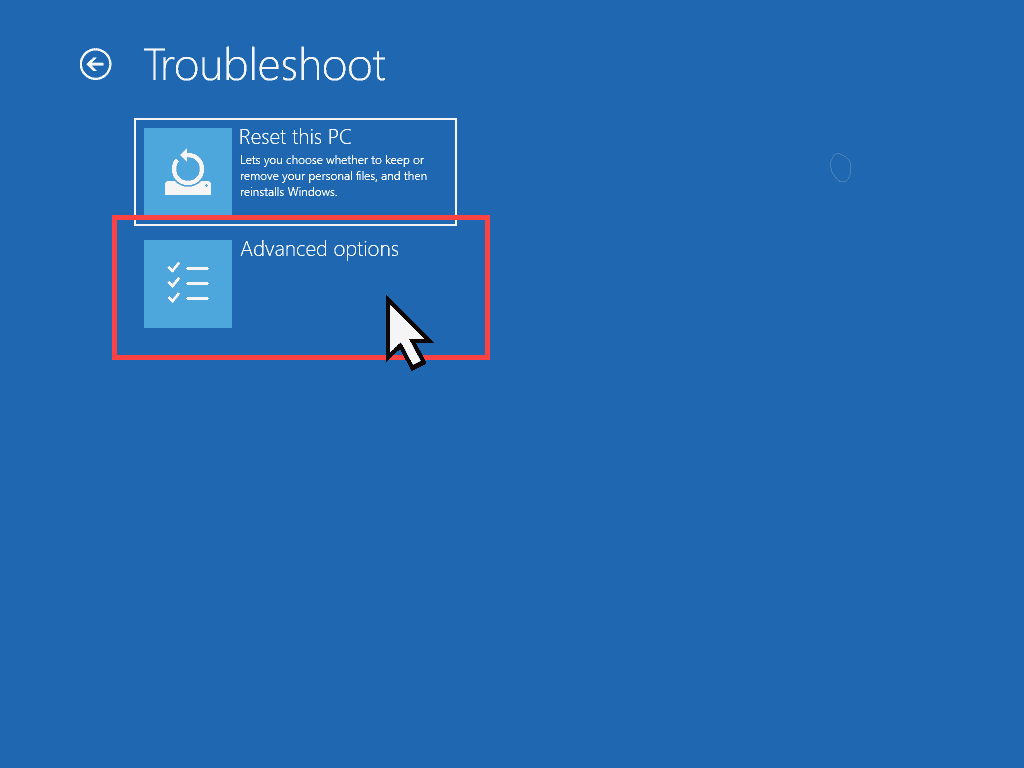
- Choose An Option – Click the Troubleshoot option.
- Troubleshoot – Click the Advanced Options.
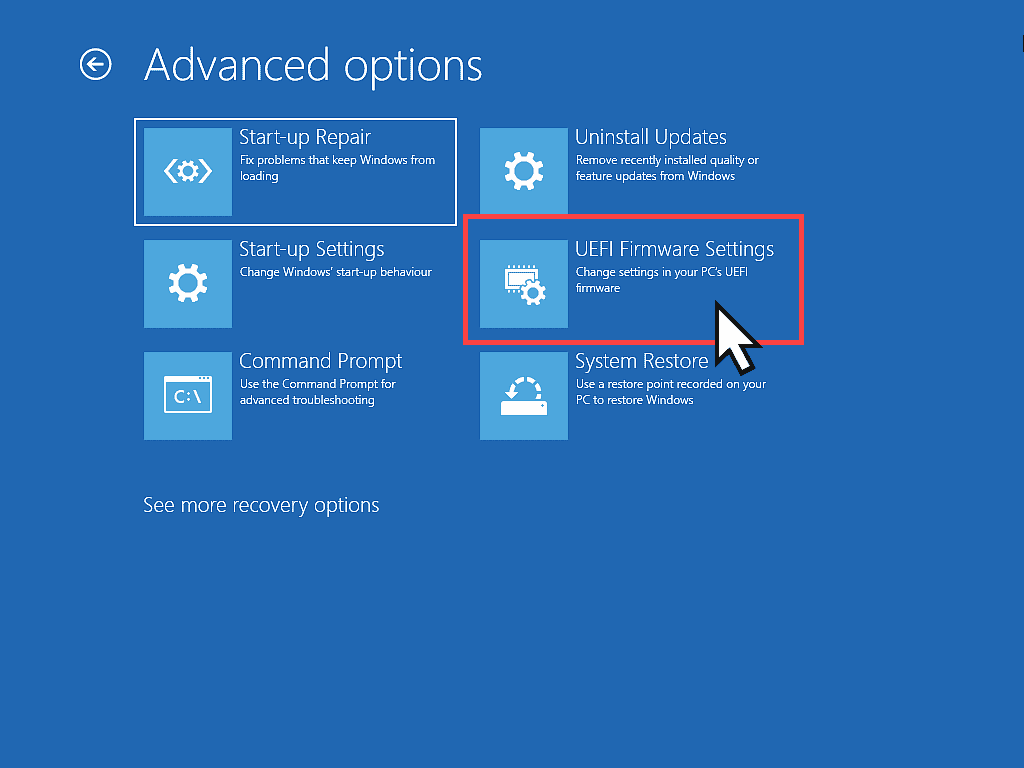
- Advanced Options – Click the UEFI Firmware Settings option.
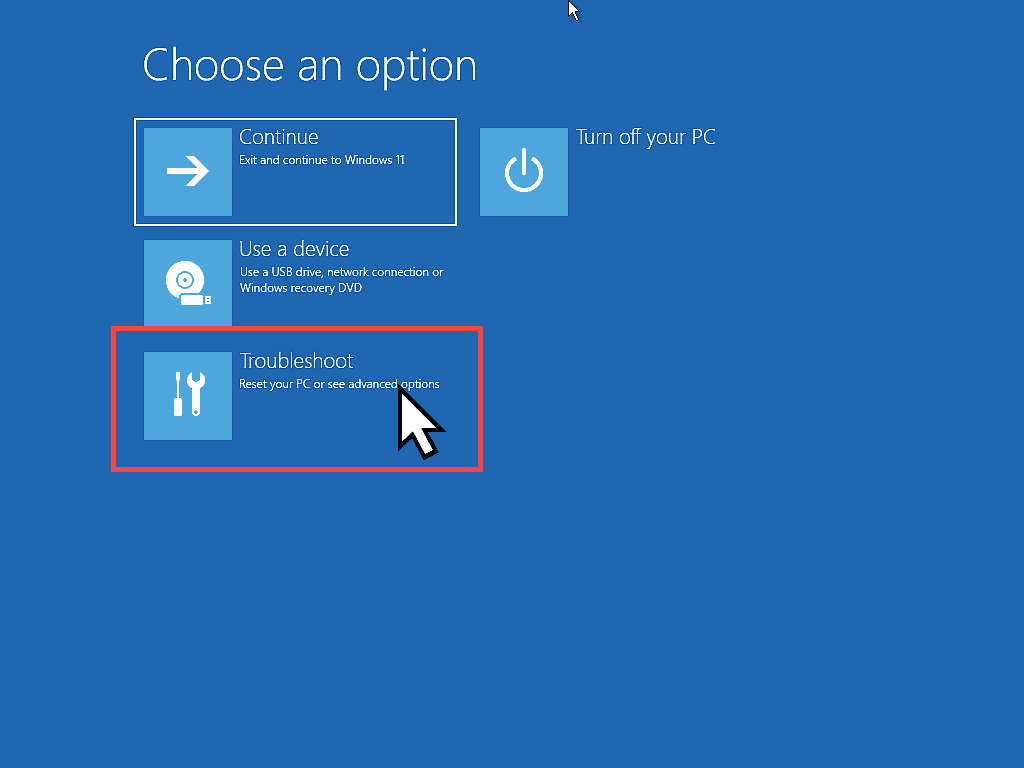
Finding The Virtualization Settings
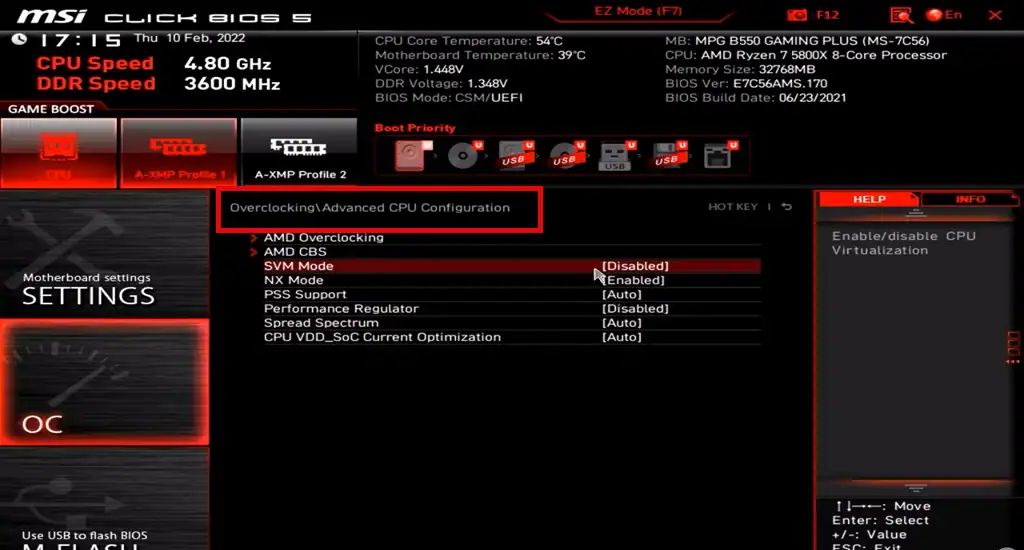
Every computer brand and motherboard manufacturer have a slightly different looking UEFI/BIOS. That makes things a little more difficult, but not impossible. The settings you need will usually be located in a sub menu. Look for an Advanced tab/menu or Configuration tab.
Inside that menu you’ll need to open the CPU menu, or setup tab. Look for one of these settings depending on your processor (CPU) and enable it –
- For Intel Processors: Look for “Intel Virtualization Technology,” “Intel VT-x,” or “VMX.”
- For AMD Processors: Look for “SVM Mode,” “Secure Virtual Machine” or “AMD-V,”
With virtualization enabled hit the F10 key on your keyboard to save and exit the BIOS.
Virtualise Everything
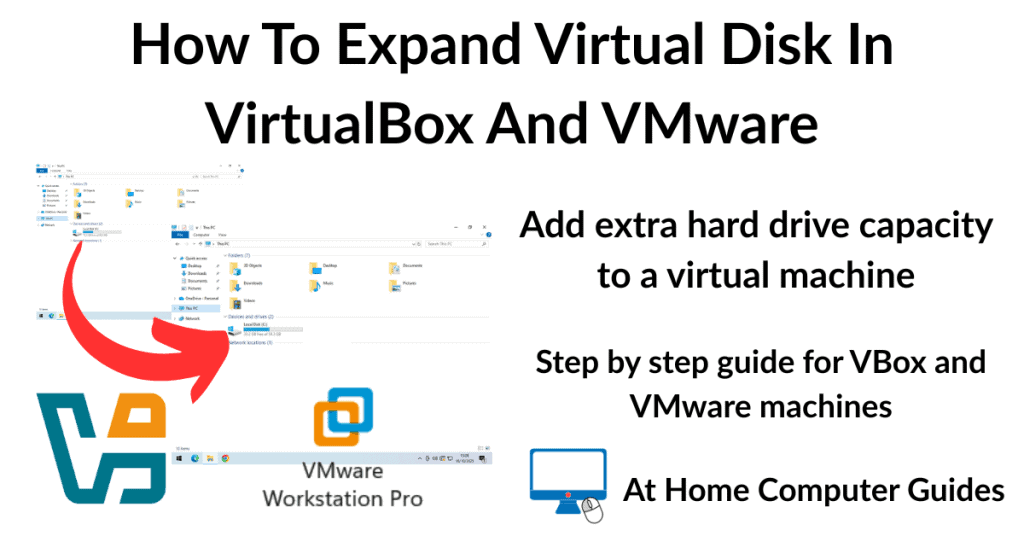
To create a virtual machine (virtual computer) you’ll need to choose what’s known as a hypervisor. A hypervisor is the program that emulates the hardware of a computer. There’re two main contenders, VMware Workstation Pro and VirtualBox. Both are free to use and work well.